What Best Describes Residual Lung Volume
-Allows for an uninterrupted exchange of gas between the blood and alveoli. What affects residual volume.
Lung Volumes Definitions Measuring Teachmephysiology
The tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such breath.

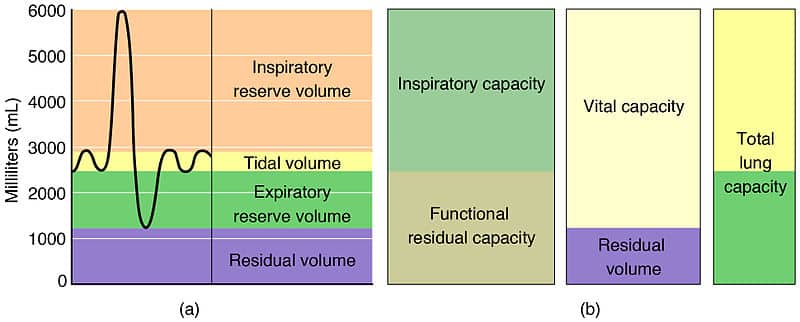
. Residual Volume Amount of air remaining in the lungs after maximum expiration about 1300 mL. The air volume between the lung tissues D. Residual volume is the only lung volume that is not decreased with respiratory muscle weakness.
The air volume normally in the lungs B. - Prevents the lungs from being fully emptied. Sets found in the same folder AP Lecture Section 3 89 terms alysiavanwormer Blood Cells APR Module 9 30 terms.
The air volume in the lungs after. The residual volume is about the total volume of air around 1100 ml to 1200 ml residing in the lungs after the reserve volume is emitted or breathed out. What statement best describes tidal volume.
The volume of air still remaining in the lungs after the most forcible expiration possible and amounting usually to 60 to 100 cubic inches 980 to 1640 cubic centimeters called also residual air. Hence vital capacity is equal to the total lung capacity minus residual volume. The air volume in the lungs after.
10 34 47 80 However residual volume can be unchanged despite expiratory muscle weakness. The air volume remaining in the lungs even after exhaling as deeply as possible D. Which of the following best describes residual lung volume.
The air volume remaining in the lungs after exhaling as deeply as possible What term is given to the ratio of alveolar ventilation to pulmonary blood flow. Total lung capacity TLC is the total volume of air present in the lungs after forced inspiration. Residual volume is determined by competing factors.
Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs at the end of a maximal expiration and is typically increased due to the inability to forcibly expire and remove air from the lungs. The air volume remaining in the lungs even after exhaling as deeply as possible Which of the following does not contribute to inspiration and expiration. Medical Definition of residual volume.
Body plethysmography uses Boyles Law to determine lung volumes whereas inert gas dilution and nitrogen washout use. Which of the following best describes residual lung volume. The air volume between the lung tissues C.
FRC is typically measured by one of three methods. The volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximal expiratory effort is the residual volume RV. The air volume remaining in the lungs even after.
After a normal exhalation continuing to exhale and forcing as much air as possible from the lung 10-15 L Forced vital capacity. Some lung volumes can be measured during spirometry. TLC ERV IRV TV RV or VC RV.
Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs at the end of a maximal expiration and is typically increased due to the inability to forcibly expire and remove air from the lungs. However measurement of the residual volume RV functional residual capacity FRC and total lung capacity TLC requires special techniques. The dynamic lung volumes are mostly derived from vital capacity.
Tidal breathing is normal resting breathing. -prevents fluctuations in blood gases during phases of the breathing cycle including deep breathing. Expiratory Reserve Volume Amount of air that can be exhaled with maximum effort about 1200 mL.
The air volume. The lung capacity of a. QUESTION 7 Which of the following best describes residual lung volume.
The air volume between the lung tissues D. The total lung capacity applies to the total volume of air-filled in the lungs after a forced inspiration. Also what are the 4 lung volumes.
The average human respiratory rate is 3060 breaths per. The air volume in the lungs after inhaling as deeply as possible C. Does a persons height affect their lung capacity.
The static lung volumescapacities are further subdivided into four standard volumes tidal inspiratory reserve expiratory reserve and residual volumes and four standard capacities inspiratory functional residual vital and total. The residual lung volume serves an important physiologic function because it. Compare supplemental air.
The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air. Tidal volume is the air exchanged during normal breathing. The air volume normally in the lungs B.
The lung capacities can be explained by the following terms. Inspiratory functional residual vital and total lung capacities. Drag the label to the term that describes it.
FVC and FEV1 decline with age while volumes and capacities such as RV and FRC increase. QUESTION 69 Which of the following best describes residual lung volume. Total volume of air voluntarily moved in one breath includes TV plus IRV and ERV 4-5 L in young men and 3-4 L in young women.
It is equal to the sum of IRV ERV and TV and the residual volume RV. Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle. 33 48 This occurs if there is a corresponding decrease in the tendency for the chest wall to recoil out to.

Residual Volume An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Breathing Capacity Biology For Majors Ii

Lung Volumes And Capacities Volume And Capacity Human Anatomy And Physiology Nursing School Studying
0 Response to "What Best Describes Residual Lung Volume"
Post a Comment